Category: Power Wheelchair
Posted by 2026-01-03 10:01
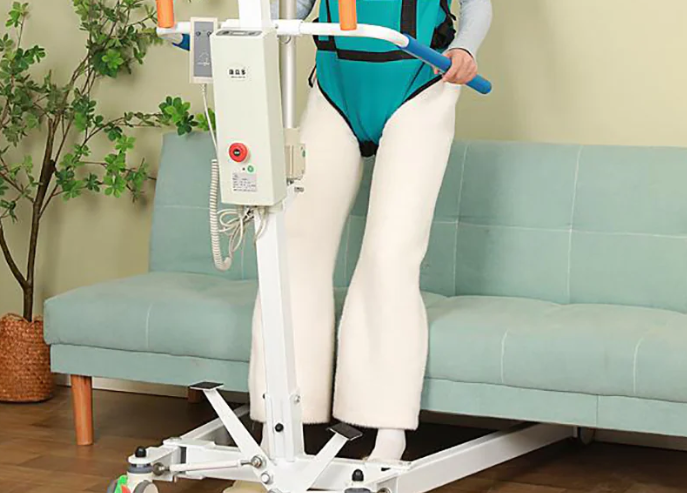
hoyer lift legs
In-Depth Analysis of Hoyer Lift Base Leg Systems: The Engineering Art of Stability
The base leg system of a Hoyer Lift is the core of the equipment’s stability. This seemingly simple structure embodies sophisticated engineering design and safety considerations. hoyer lift legs Understanding the principles of the leg system and proper usage methods is key to ensuring safe and reliable transfers every time.
Principles of Leg System Design
Mechanical Fundamentals
Stability Triangle: The legs form a stable triangular support structure.
Center of Gravity Control: Scientific calculations ensure the center of gravity remains within the support range.
Torque Balance: Precise weight distribution and application of lever principles.
Materials Science: Combination of high-strength steel and optimized structural design.
Safety Factors
Static Load: A safety factor of 3–5 times the designed load capacity.
Dynamic Load: Consideration of dynamic forces during movement and lifting.
Accidental Impact: Reserved additional strength for unexpected scenarios.
Fatigue Life: Ensuring structural integrity for long-term use.
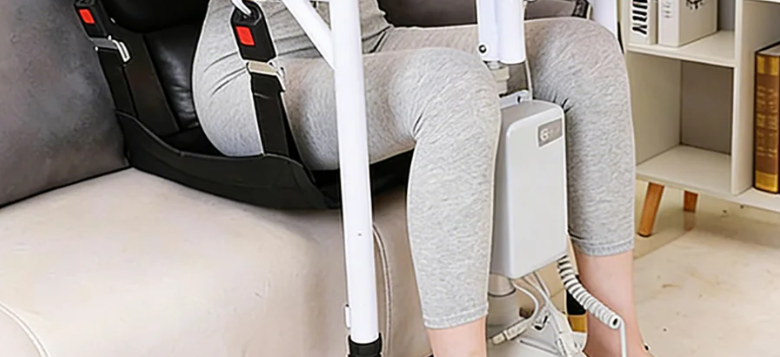
Detailed Explanation of Leg Types hoyer lift legs
H-Type Base System
Structural Features
Four legs form a rectangular support.
Front and rear legs are connected by crossbars.
Provides the most stable support foundation.
Advantages
Excellent lateral stability.
Suitable for heavyweight patients.
Simple and intuitive operation.
Limitations
Requires a large operating space.
Takes up more space during storage.
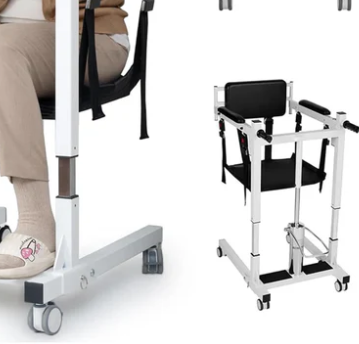
U-Type Base System
Innovative Design
Open-front design.
Legs extend backward.
Optimized access angle.
Usage Advantages
Easy access to patients from the side of the bed.
Better adaptability in narrow spaces.
Easier operation around obstacles.
Applicable Scenarios
Home care environments.
Space-constrained areas.
Situations requiring side access to patients.
Adjustable Width Design
Technical Features
Manual or automatic width adjustment.
Locking devices for safety.
Visual or tactile position indicators.
Practical Value
Adapts to different bed widths and spaces.
Facilitates passage through narrow doorways.
Optimizes space utilization during storage.
Safety Features of Legs
Anti-Tipping Mechanisms
Automatic Stabilization: Technology for automatic adjustment of the center of gravity.
Leg Locking: Multi-position locking to ensure stability.
Overload Protection: Structural safety redundancy design.
Tilt Warning: Tilt alert systems for intelligent models.
Wheel and Brake Systems
Caster Design
Swivel front casters and fixed rear casters.
Appropriate wheel size and material.
Smooth rotation and rolling performance.
Brake Mechanisms
Independent brakes for each wheel.
One-foot operated dual-directional brakes.
Quick locking for emergency situations.
Leg Management During Operation
Correct Positioning Process
Access Angle: Approach the bed edge at a 30–45 degree angle.
Leg Deployment: Ensure legs are fully extended and locked.
Under-Bed Extension: Front legs should fully extend under the bed.
Space Check: Confirm legs do not come into contact with obstacles.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Legs not fully extended.
❌ Using the lift on soft surfaces.
❌ Ignoring the impact of height differences.
❌ Overloading the equipment.
Space Requirement Guidelines
Minimum Operating Space: 1.5m × 1.5m.
Doorway Passage Width: At least 80cm.
Turning Radius: Account for the swing space of the legs.
Storage Space: Consider the dimensions of the lift in its folded state.
Adaptation to Special Environments
Different Floor Conditions
Hard Floors
Ensure wheel brakes function effectively.
Check the condition of anti-slip pads on the legs.
Pay attention to floor flatness.
Carpeted Floors
Confirm the carpet does not hinder movement.
Check if legs will sink into the carpet.
Consider using protective pads.
Uneven Floors
Avoid operating on uneven surfaces.
Use shims to level the lift.
Consider selecting specialized models.
Solutions for Narrow Spaces
Leg Adjustment: Utilize the adjustable width function.
Operation Techniques: Master small-space turning methods.
Environment Modification: Implement necessary space optimization measures.
Equipment Selection: Choose compact designs.
Maintenance and Inspection Key Points
Daily Inspection Checklist
Leg locking mechanisms function normally.
No deformation or damage to the legs.
Wheels rotate flexibly without jamming.
Brake systems work reliably.
Leg adjustment mechanisms operate smoothly.
Regular Maintenance Items
Weekly: Clean legs and connecting mechanisms.
Monthly: Inspect all structural connection points.
Quarterly: Professional inspection of leg structural integrity.
Annually: Comprehensive maintenance and safety testing.
Fault Identification and Handling
Legs Unable to Lock: Inspect locking mechanisms and springs.
Difficulty Moving: Check wheels and leg alignment.
Abnormal Noise: Inspect connection points and bearings.
Visible Deformation: Immediately stop use and repair.
Trends in Technological Innovation
Intelligent Leg Systems
Automatic Leveling: Automatic adjustment to adapt to uneven floors.
Obstacle Detection: Sensors to detect and avoid obstacles.
Weight Sensing: Real-time monitoring of weight distribution.
Remote Locking: Wireless control of leg positions.
Advances in Materials Science
Composite Materials: Lighter yet stronger leg materials.
Surface Treatment: Enhanced wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant coatings.
Connection Technology: More reliable structural connection methods.
Folding Mechanisms: More compact storage designs.
Selection Guide
Selection Based on Usage Environment
Spacious Spaces: Standard H-type bases offer optimal stability.
Narrow Environments: hoyer lift legs U-type or adjustable-width bases are more suitable.
Multi-Scenario Use: Adjustable-width models are the most flexible.
Heavy-Duty Needs: Reinforced leg designs.
Selection Based on User Needs
Frequent Transfers: Prioritize ease of operation.
Multiple Locations: Leg designs requiring adaptability.
Caregiver Physical Strength: Lighter equipment for easier operation.
Long-Term Use: Prioritize durability and reliability.
Safety Usage Culture
Training Focus
Correct operation methods for the leg system.
Risk identification and prevention measures.
Emergency handling procedures.
Regular inspection and maintenance skills.
Safety Awareness
Inspect leg status before each use.
Understand the equipment’s load limits.
Cultivate cautious operation habits.
Establish mechanisms for reporting and addressing issues.
Conclusion
The leg system of a Hoyer Lift is the cornerstone of the equipment’s safe operation, and its importance cannot be overlooked. hoyer lift legs By deeply understanding the design principles of the leg system, mastering correct operation methods, and implementing strict maintenance procedures, we can ensure this critical support system remains in optimal condition at all times. Remember, in the precise and safety-critical task of patient transfer, a stable foundation is the prerequisite for everything. Investing time in learning and paying attention to the details of the leg system is the best investment in safe care.